What is Selection Sort?
Selection sort is an in-place sorting algorithm that selects data appropriate for a position from all unsorted data and exchanges positions. It proceeds with the following steps:
- 1) Find the data with the smallest value among the given data list.
- 2) Replace the found data with the position of the data located at the very beginning.
- 3) Replace the remaining data excluding the very first position in the same way.
Expressed in pseudo code, it looks like this:
For i -> 0 to n:
Among data compared from a[i] to a[n-1], if the smallest data is in a[j],
swap a[i] and a[j]
Selection Sort Process
Examining the selection sort process in detail through diagrams. The way of counting rotation count (PASS) may differ depending on whether the starting state is included (whether given as initial state or not).
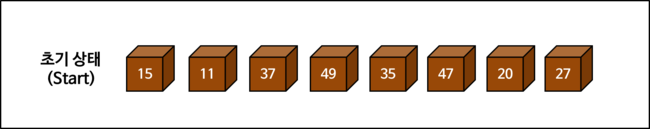


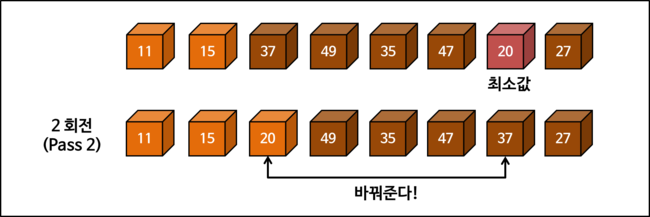
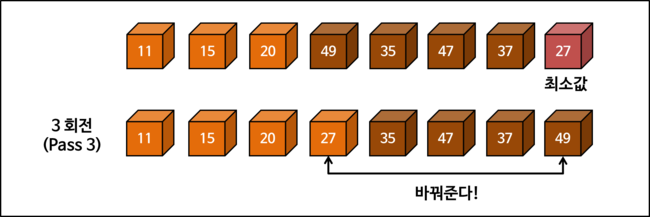

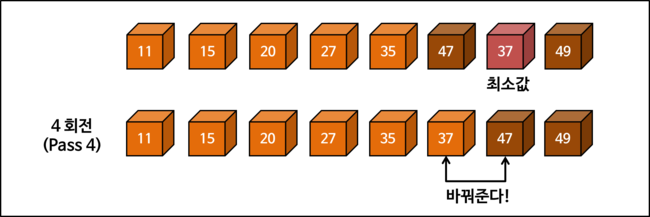


Selection Sort Implementation
Examining the above process through source code:
void selectionSort(int *list, const int n)
{
int i, j, indexMin, temp;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
indexMin = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (list[j] < list[indexMin])
{
indexMin = j;
}
}
temp = list[indexMin];
list[indexMin] = list[i];
list[i] = temp;
}
}
Performance of Selection Sort
Examining complexity: When C is the comparison count for sorting in best (min), average (ave), and worst (max) cases, it can be expressed as follows:
\[{ C }_{ min }{ =C }_{ ave }={ C }_{ max }=\sum _{ i=1 }^{ N-1 }{ N-i } =\frac { N(N-1) }{ 2 } =O({ n }^{ 2 })\]Here, N represents the number of data.