Table of Contents
- Spring Cloud Config: Introduction and Example
- Spring Cloud Config: Spring Cloud Bus Example
- Spring Cloud Config: Auto Refresh with Git Webhook
- Spring Cloud Config: Changes in Spring Boot 2.4
What If You Forget to Call refresh?
In the previous post, we used Spring Cloud Bus to avoid calling every client manually when configuration changes. But what if you update config files and forget to call the refresh endpoint?
Then clients do not receive the latest configuration values.
This is easy to solve with a Git Webhook.
Trigger a refresh event whenever config files change, so no manual endpoint call is required.
Added in January 2021: Starting from Spring Boot 2.4,
bootstrap.ymlis no longer used in the same way as in this post. Also, the actuator endpointbus-refreshused here changed tobusrefresh. See the fourth article in the table of contents: “Changes in Spring Boot 2.4”.
What Does the Architecture Look Like?
Before coding, review the flow.
Whenever a config file change is pushed to Git, a webhook event is sent to a registered application.
In this post, we use the Spring Cloud Config Server /monitor endpoint.
The Config Server receives the event, fetches the latest config from Git,
and publishes a refresh event to Spring Cloud Bus.
All clients are connected to Spring Cloud Bus and receive that event.
Because each client has actuator, it can handle the refresh event directly.
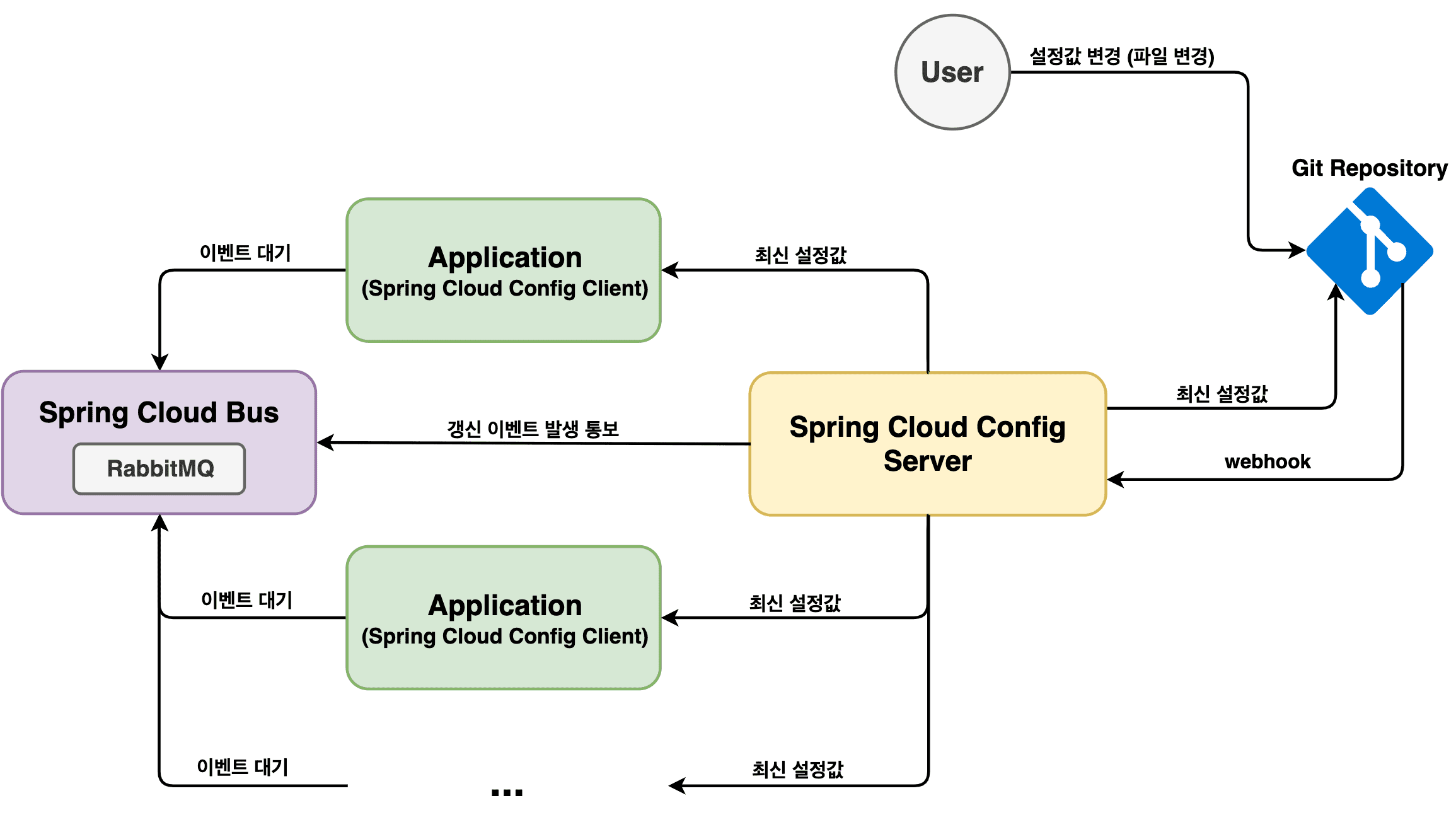
Then all beans under @RefreshScope are refreshed with updated values.
Config clients request the latest values from the Config Server,
and the Config Server updates itself using the latest state from Git.
So clients receive updated configuration on the next fetch.
Let’s apply this step by step.
All sample code is in GitHub. See links at the bottom.
Message Broker Setup
As before, we use the same broker as the previous post.
Reuse the RabbitMQ container launched with Docker.
Ports remain the same: 5672 for integration and 8087 for management UI.
$ docker run -d --name rabbitmq \
-p 5672:5672 -p 8087:15672 \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=madplay \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=madplay \
rabbitmq:management
If the container starts successfully, open http://localhost:8087 and verify the admin page.
Update Spring Cloud Config Server
No changes are required on config clients in this step.
Only Config Server settings need updates.
First, add these dependencies in pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-monitor</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring-cloud-config-monitor dependency
The spring-cloud-config-monitor dependency provides the /monitor endpoint
so the Config Server can receive repository change events such as Git push.
It handles events only when spring.cloud.bus is enabled.
The default is false, so set it to true.
Add this to Config Server application.yml:
spring:
# ... omitted
bus: # add this section
enabled: true
Spring Cloud Stream
Spring Cloud Stream supports message-driven and event-driven microservices. It delivers events through brokers such as RabbitMQ and Kafka.
This clarifies the relationship with Spring Cloud Bus: Spring Cloud Bus connects applications through a message broker and broadcasts events. Spring Cloud Bus is built on Spring Cloud Stream.
The spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit dependency added above selects
the Spring Cloud Stream implementation that uses RabbitMQ as the default broker.
So to use the broker from Config Server, add:
spring:
# ... omitted
rabbitmq: # add this section
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: madplay
password: madplay
Final application.yml:
server:
port: 8088
spring:
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/madplay/spring-cloud-config-repository
bus:
enabled: true
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: madplay
password: madplay
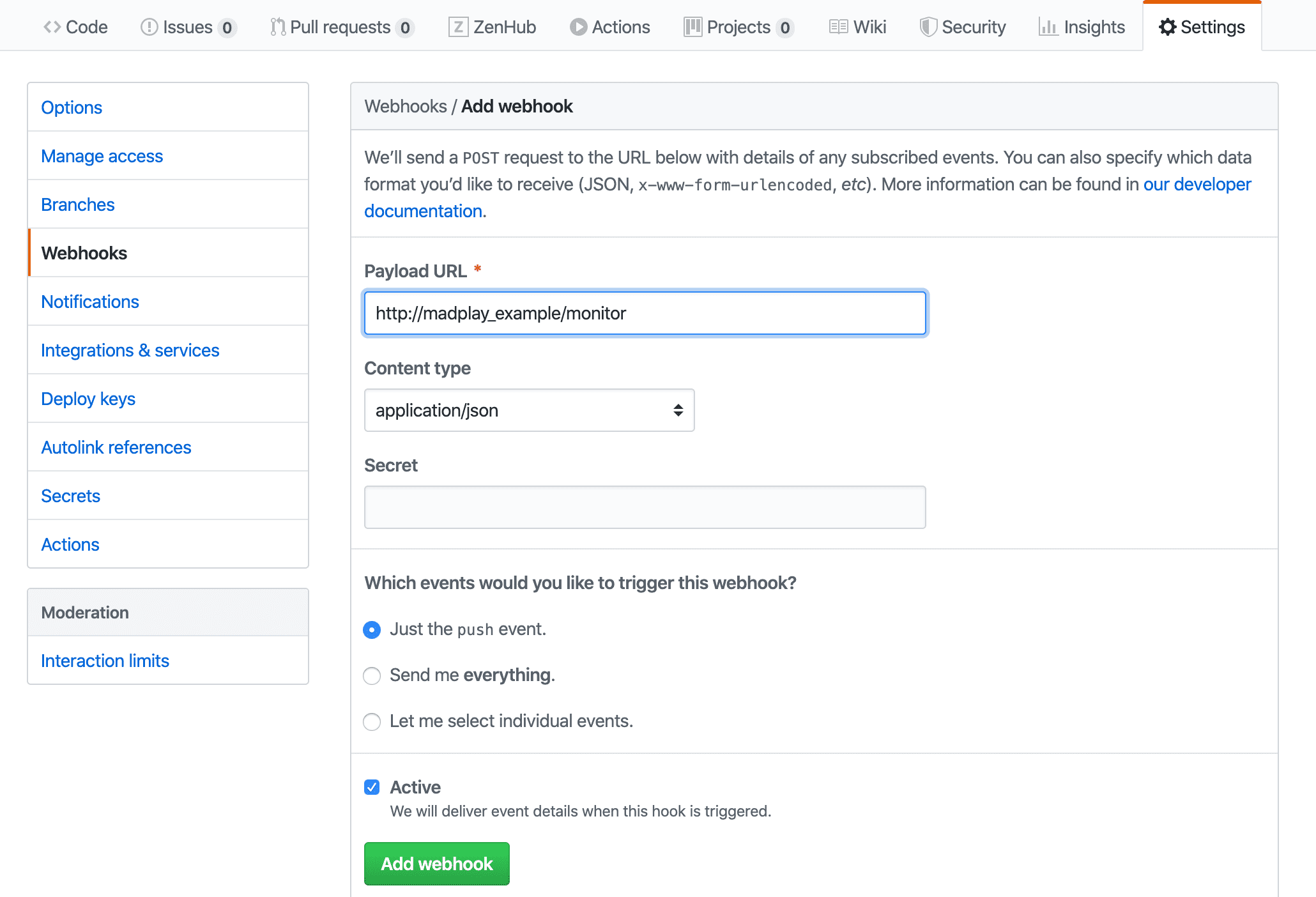
Add a Webhook to GitHub Repository
You can register the /monitor endpoint URL as a webhook in the Git repository.
This requires a domain or public IP. localhost is not reachable from GitHub.
In this example, testing is done locally because there is no public endpoint.
If you can register it, add webhook settings like below.
Run the Test
Start all applications and verify ports:
- Port 8086: Config Client 2
- Port 8087: RabbitMQ
- Port 8088: Config Server
- Port 8089: Config Client 1
As in the previous post, call each client and check current config values.
$ curl -X GET "http://localhost:8089/dynamic"
# result
{
"profile": "I'm dev taeng",
"comment": "Hello! updated by Spring Bus."
}
$ curl -X GET "http://localhost:8086/dynamic"
# result
{
"profile": "I'm dev taeng",
"comment": "Hello! updated by Spring Bus."
}
After checking both clients, modify config-dev.yml in the Git repository,
then commit and push.
taeng:
profile: I'm dev taeng
comment: Hello! updated by Spring Bus with webhook!
If your webhook is registered with a public endpoint, /monitor is triggered automatically.
Because this example uses localhost, call /monitor manually:
$ curl -v -X POST "http://localhost:8088/monitor" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "X-Event-Key: repo:push" \
-H "X-Hook-UUID: webhook-uuid" \
-d '{"push": {"changes": []} }'
Note: Unnecessary use of -X or --request, POST is already inferred.
* Trying ::1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8088 (#0)
> POST /monitor HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8088
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.1
> Accept: */*
> Content-Type: application/json
> X-Event-Key: repo:push
> X-Hook-UUID: webhook-uuid
> Content-Length: 26
>
* upload completely sent off: 26 out of 26 bytes
< HTTP/1.1 200
< Content-Type: application/json
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
< Date: Tue, 11 Feb 2020 14:43:28 GMT
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
["*"]* Closing connection 0
Now call each client again and verify updated values.
$ curl -X GET "http://localhost:8089/dynamic"
# result
{
"profile": "I'm dev taeng",
"comment": "Hello! updated by Spring Bus with webhook!"
}
$ curl -X GET "http://localhost:8086/dynamic"
# result
{
"profile": "I'm dev taeng",
"comment": "Hello! updated by Spring Bus with webhook!"
}
As with /actuator/bus-refresh, all clients are refreshed.
You can also confirm this in server/client logs when /monitor is called.
# Server log
Refresh for: *
No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
Started application in 0.148 seconds (JVM running for 568.284)
Fetched for remote master and found 1 updates
Adding property source: file:/var/folders/7b/4vlwnfvd5r54h9fdd89qtnqm0000gn/T/config-repo-8303556801916876626/config-dev.yml
Adding property source: file:/var/folders/7b/4vlwnfvd5r54h9fdd89qtnqm0000gn/T/config-repo-8303556801916876626/config-dev.yml
Received remote refresh request. Keys refreshed []
# Client1 log
Fetching config from server at : http://localhost:8088
Located environment: name=config, profiles=[dev], label=null, version=36df45a532624d91f5e63f5f463b6d4becf97fc6, state=null
Located property source: [BootstrapPropertySource {name='bootstrapProperties-configClient'},
BootstrapPropertySource {name='bootstrapProperties-https://github.com/madplay/spring-cloud-config-repository/config-dev.yml'}]
The following profiles are active: dev
Started application in 2.879 seconds (JVM running for 527.944)
Received remote refresh request. Keys refreshed [config.client.version, taeng.comment]
# Client2 log
Fetching config from server at : http://localhost:8088
Located environment: name=config, profiles=[dev], label=null, version=36df45a532624d91f5e63f5f463b6d4becf97fc6, state=null
Located property source: [BootstrapPropertySource {name='bootstrapProperties-configClient'},
BootstrapPropertySource {name='bootstrapProperties-https://github.com/madplay/spring-cloud-config-repository/config-dev.yml'}]
The following profiles are active: dev
Started application in 2.145 seconds (JVM running for 494.962)
Received remote refresh request. Keys refreshed [config.client.version, taeng.comment]
Closing
In the previous post, Spring Cloud Bus let us refresh all connected clients with one endpoint call.
In this post, we automated even that manual call using a Git Webhook.
In some systems, automating endpoint calls may be unnecessary.
Apply it based on operational needs.
Added in January 2021: For Spring Boot 2.4 changes, see “Changes in Spring Boot 2.4”.
All sample code used in this post:
- config server & config client
- config repository