Binary Tree
Before learning about Binary Search Tree, we must first know what a Binary Tree is. The definition is empty, or a collection of one root and nodes with two different values.
To explain more, when gradually moving from the top root node toward lower subtree directions, it means that each node that newly becomes a root has 2 or fewer child nodes.
Terms Related to Trees
There are various types of binary trees we examined earlier. They each have different definitions depending on tree structure. Before learning about tree types, first learning about terms used when describing trees:
- Directed Edge is a path from parent nodes to child nodes
- Root Node is a node without a parent, trees have only one root node.
- Leaf Node is a node without children
- Depth of each node is the length of the path from the root node to itself
- Degree is the number of child nodes a specific node has
- Tree height is the length of the path from the root node to the deepest node, trees with only root nodes have height 0.
- Sibling Node is a node with the same parent
Types of Trees
Learning about types of binary trees:
- Rooted Binary Tree : A tree with a root where all nodes have at most 2 child nodes
- Full Binary Tree : A tree where all nodes that aren’t leaf nodes have 2 child nodes
- Perfect Binary Tree : A Full Binary Tree where all leaf nodes have the same depth
- Complete Binary Tree : A binary tree where all nodes are filled except the end parts
There are also Infinite Complete Binary Tree, Balanced Binary Tree, and Degenerate Tree, etc. Examining them in more detail through diagrams:
Binary Tree
The definition of Binary Tree is that all nodes must have two or fewer child nodes. That is, it refers to trees where all nodes have degree 2 or less. And all subtrees of binary trees are all binary trees.
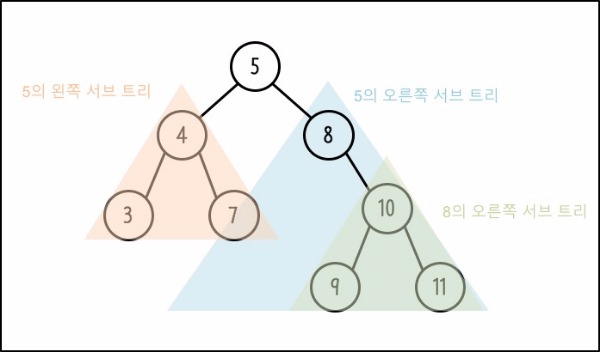
Node 5’s subtrees are trees with root 4 and root 8. Also, node 8 has a right subtree with root 10.
Applying tree-related terms we examined earlier, the height of the above tree becomes 3. When root depth is 0, count paths to the deepest nodes 9, 11. Also, node 4’s degree is 2, and leaf nodes without children are 3, 7, 9, 11.
Complete Binary Tree
Next, examining Complete Binary Tree. It refers to a tree where all nodes are filled except the last node.
Also, it refers to a tree where nodes are filled from left to right at the last level.
Perfect Binary Tree
Finally, examining Perfect Binary Tree.
All nodes must be full. Whether left or right, they must be full.
Complete Binary Trees cannot become Perfect Binary Trees, but Perfect Binary Trees can be called Complete Binary Trees.
Binary Search Tree
Binary Search Tree is a binary tree. But it has a more detailed definition.
- 1) If not empty, all nodes have different values (Keys).
- 2) Values included in the left subtree, if they exist, always have values smaller than the root’s value.
- 3) Values included in the right subtree, if they exist, always have values larger than the root’s value.
- 4) Left and right subtrees must each be another Binary Search Tree structure with root nodes.
Insertion and Deletion of Binary Search Tree
Examining operations of inserting new nodes into Binary Search Tree or deleting specific nodes:
Insertion Operation
Insertion Operation requires a process of searching for where new nodes will be located.
- 1-1) If the root node has no value, the tree doesn’t exist, so put it in the root.
- 1-2) If the root has a value and the value to insert is smaller than the root, search left.
- 1-3) If the root has a value and the value to insert is larger than the root, search right.
- 2) When proceeding with search in that direction, if there’s no value at the search location, add a node at that location.
Deletion Operation
Deletion Operation is a bit trickier than insertion operations. It needs to be distinguished according to characteristics of nodes to delete.
- 1) First, start search comparing the value of the node to delete from the root.
- 1-1) If the value of the node to delete is smaller than the root, search left and change the current pointer to the left node.
- 1-2) If the value of the node to delete is larger than the root, search right and change the current pointer to the right node.
- 2-1) When the node to delete is a leaf node
- 2-1-1) If the deletion target is a leaf node and is the parent node’s left child node, make the parent node’s left child NULL.
- 2-1-2) If the deletion target is a leaf node and is the parent node’s right child node, make the parent node’s right child NULL.
- 2-2) When the node to delete has only one child node
- 2-2-1) If it only has a right child node, attach its right child node to the deletion target node’s parent.
- 2-2-2) If it only has a left child node, attach its left child node to the deletion target node’s parent.
- 2-3) When the node to delete has all child nodes
- 2-3-1) Must select a value most similar to the node to be deleted. This way, Binary Search Tree is maintained without moving other nodes.
- 2-4-1) Select the largest value in the deletion target’s left subtree.
- 2-4-2) Select the smallest value in the deletion target’s right subtree.
Search of Binary Search Tree
Search refers to visiting all nodes of a binary tree. Representative search methods include pre-order, post-order, and in-order.
- Pre-order Search : Visits in order of my node, left child node, right child node.
- Post-order Search : Visits in order of left child node, right child node, my node.
- In-order Search : Visits in order of left child node, my node, right child node.
In Summary
In this post, we learned about Binary Search Tree. In the following post, we learn about methods for implementing Binary Search Tree.