What is Endian?
Endian refers to a method of arranging multiple consecutive objects in a one-dimensional space like computer memory. It’s said to come from a heated debate between people who break eggs from the blunt end first (Big Endian) and people who break them from the pointed end first (Little Endian), which is the opposite.
“You can find the word Endian in the Lilliput story from British novelist Jonathan Swift’s < Gulliver’s Travels >.”
Endian in Computer Science
The term Endian in computer science is said to originate from an article written by Danny Cohen in 1980 called < On Holy Wars and a Plea for Peace >.
“…which bit should travel first, the bit from the little end of the world, or the bit from the big end of the word? The followers of the former approach are called the Little-Endians, and the followers of the latter are called the Big-Endians.”
If rewritten from a computer science perspective, End should be interpreted as goal or target rather than meaning end.
On the other hand, Endian, as mentioned earlier, refers to a method of arranging multiple consecutive objects in a one-dimensional space like memory, and especially, the method of arranging bytes is called Byte Order. It can generally be divided into Big-Endian where large units come first and Little-Endian where small units come first.
Endian by System
Not all systems use the same endian. Linux and Windows systems use Little Endian. So we usually use systems that use Little Endian.
However, conversely, transmission through networks is Big Endian. After IP packets are divided by byte units, the Most Significant Bit is sent first and the Least Significant Bit is sent later. Also, the bit transmission order within bytes sends the Most Significant Bit first. Overall, it can be viewed as Big Endian order.
Big-Endian
Big Endian where large units come first.
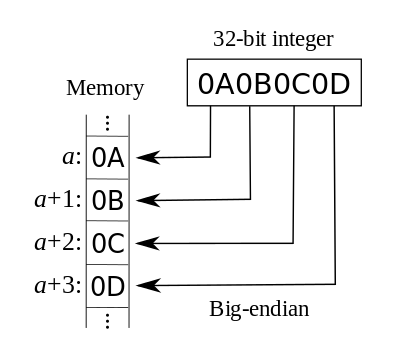
The advantage is that it’s easy for humans to read. This is because it’s the same way we write and read numbers. For example, 0x12345678 is expressed as 12 34 56 78 in Big Endian.
Little-Endian
Little Endian where small units come first.
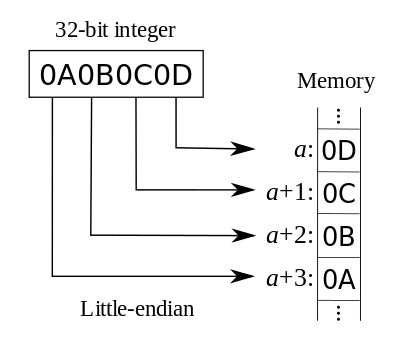
As shown in the figure, it’s stored from right to left. This is the same order as arithmetic operations being processed from lower memory addresses to higher addresses.
Even/odd checking is also fast. This is because you only need to check the first byte. Intel and AMD CPUs that we commonly use employ this method.
Bi-Endian
On the other hand, some systems are designed to allow selection of endian, which is called Bi-Endian. Representative examples include ARM, PowerPC, DEC Alpha, MIPS, etc.