What is a File System?
A file system refers to an agreement on how to record, read, and delete data on a hard disk.
NTFS, FAT32, etc. refer to file systems used in Windows operating systems. You may have seen them when formatting.
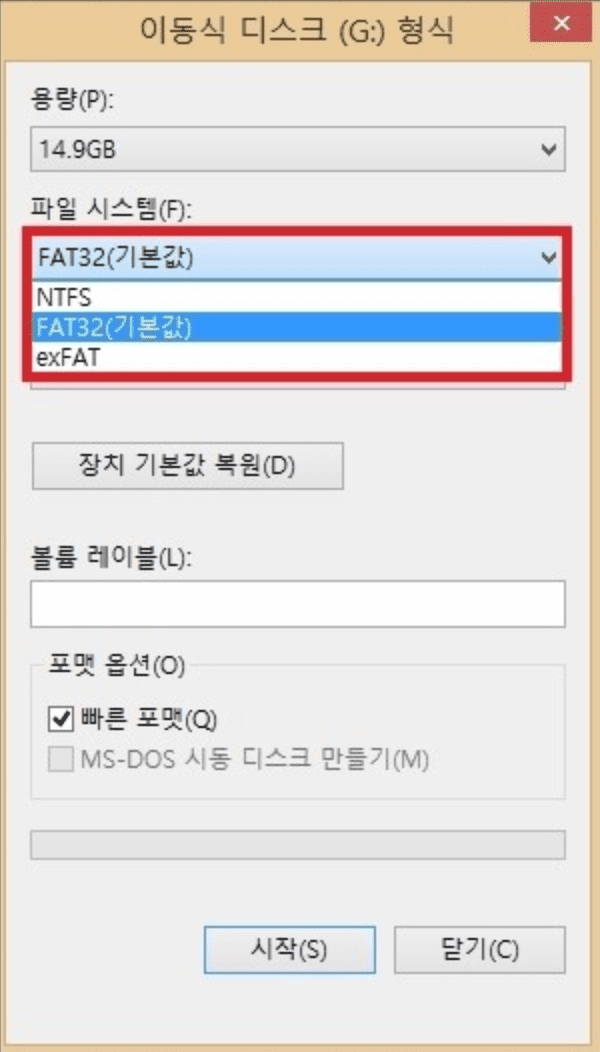
FAT32
FAT stands for File Allocation Table.
It’s generally used in memory cards or USB drives, and was also widely used in computer systems before NTFS.
A single file can only have a maximum of less than 4GB. It also has the disadvantage of having restrictions on file name length.
It only recognizes up to 32GB, so there’s the inconvenience of having to partition hard disks or SSDs that exceed this capacity.
FAT32 is compatible with outdated operating systems like Windows 98, Windows ME, as well as Linux, Mac OS, digital cameras, game devices, etc.
Actually, FAT32 can theoretically partition up to 2TB.
The reason it’s limited to 32GB is that when partitioning above 32GB, search time increases, and since there was no need to use more than 32GB at that time,
Microsoft set this limitation. Using other format tools, you can format up to 2TB with FAT32.
NTFS
NTFS stands for New Technology File System and is the file system of Windows NT series operating systems.
It was created to replace FAT32. It’s a file system included in most Windows operating systems,
and a single file can have a maximum capacity of 16 exabytes (16,777,216 TB).
NTFS is the method used in Windows XP and has excellent security. Since it was developed after FAT32, it’s superior to FAT32 in terms of safety and security.
exFAT
Additionally, looking at exFAT, this is a new file system format created by Microsoft.
It’s a FAT32 version that supports single files over 4GB. However, it has disadvantages of being slower and less stable than FAT32.
However, general users don’t need to worry about these stability issues at all.
Also, it has the advantage of being faster than NTFS when processing multiple small files, and since most PC programs read multiple fragmented files,
exFAT is quite advantageous. However, since exFAT may fail to be recognized on older models, if you don’t need to carry single files over 4GB on USB memory,
FAT32 format is advantageous. It can be recognized on all models (Windows, Linux, Unix, etc.).
In Conclusion…
In conclusion, while NTFS is the most commonly used file system, FAT32 actually has faster speed than NTFS.
So for relatively small-capacity storage media, use FAT32 format, and for large file storage or when maximum volume size exceeds 32GB,
it’s good to format with NTFS format.