Before We Start
Let’s organize a few terms. First, plaintext means the original message to protect through encryption. The encrypted result is ciphertext. Converting plaintext to ciphertext is encryption, and converting ciphertext back to plaintext is decryption.
Confusion and Diffusion
In general, secure ciphertext should not allow external attackers to easily infer the original plaintext, and the algorithm used for encryption should also be hard to infer. These principles are defined by Claude Elwood Shannon, the American mathematician and electrical engineer, through the terms confusion and diffusion.
Confusion is the property of hiding the relationship between plaintext and ciphertext. For example, even if one bit of the original message changes, ciphertext changes should not be predictable. Diffusion is the property that makes the underlying encryption algorithm hard to infer. Like confusion, a one-bit change should affect the ciphertext broadly so patterns are hard to identify.
A strong cipher needs both properties.
Substitution and Transposition Ciphers
A substitution cipher replaces characters with other characters. It strengthens confusion by making original content harder to infer. Here, plaintext and ciphertext characters do not need strict one-to-one mapping.
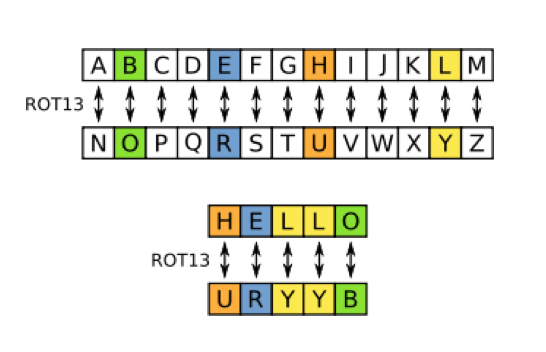
The figure below shows ROT13 (Rotate by 13).
It is a Caesar substitution cipher variant that shifts each alphabet letter by 13.
For example, HELLO becomes URYYB.
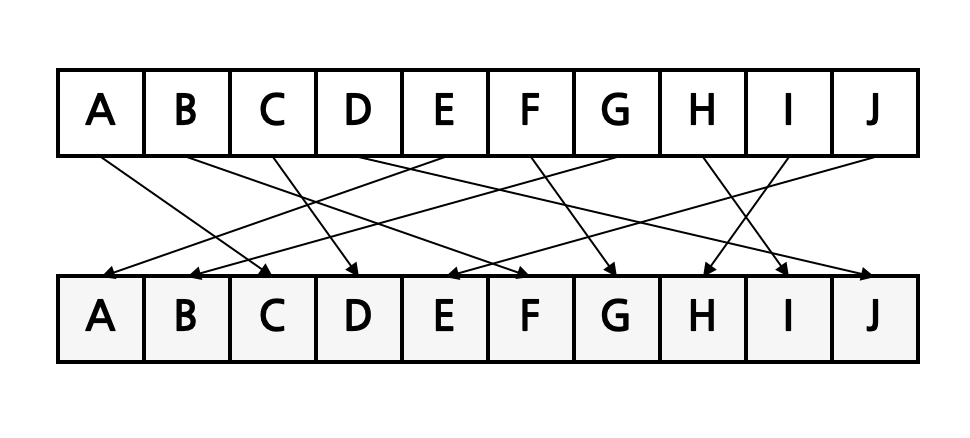
Next, a transposition cipher rearranges character order according to defined rules. It strengthens diffusion by making encryption behavior harder to infer. Characters used in plaintext and ciphertext are in one-to-one correspondence.
Block Ciphers and Stream Ciphers
A block cipher is a class of methods that process fixed-size groups of bits at a time. That group is called a block, and its size is block length.
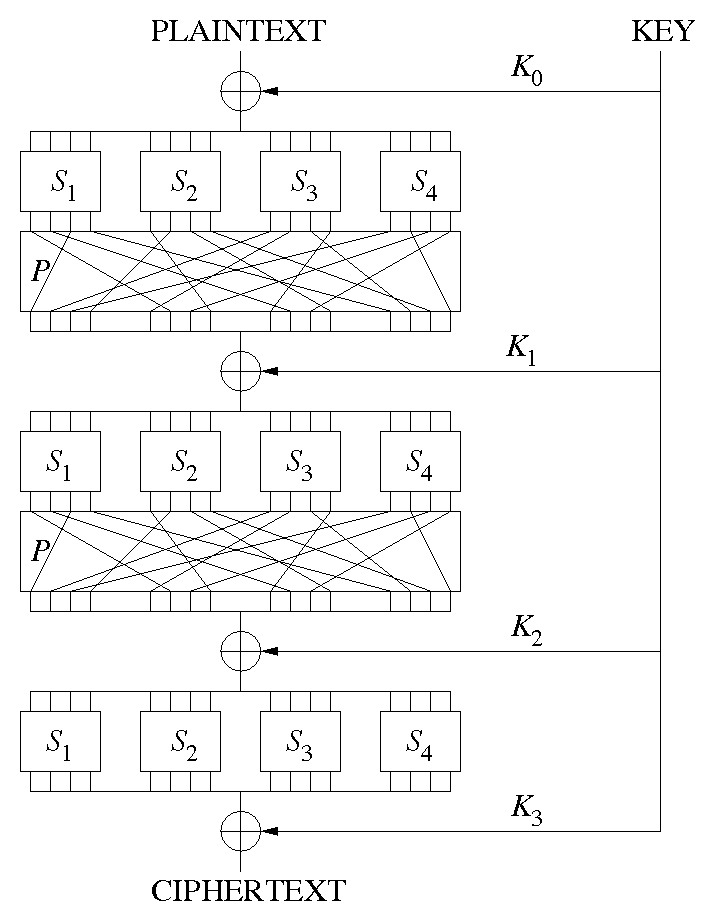
Block cipher structures include Feistel structure and Substitution-Permutation Network (SPN). Below is SPN, which combines substitution and permutation to implement confusion and diffusion.
There is often terminology confusion. Substitution means replacement, and permutation means reordering. In Korean translations, the terms can overlap, so this post follows Wikipedia terminology.
A stream cipher encrypts continuous bits or bytes sequentially. Unlike block ciphers that process grouped bits independently of sequence, stream ciphers proceed in sequence and typically carry continuity where previous results affect subsequent encryption.
Representative algorithms include RC4, A5/1, and A5/2. The figure below shows the structure of RC4 stream cipher.